| Determining Perimeter & Area |
 |
| Determining Perimeter & Area |
 |
| Suppose you have a yard and want to put up a fence. You need to know how much fencing material to purchase, so you must know the length around the yard, or its perimeter. If you want to lay down sod, you would want to know how much sod you need for the project by determining the size or area of the yard. Because the shape of things (like yards) vary, it is important to understand how to find out where to begin measuring. The following information details how to find the perimeter and area of the most common shapes. For more detailed explanations of these concepts go to the links at the bottom of this page. |
![]()
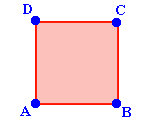 |
Square
The perimeter of a square
is equal to 4 times the length of a side.
|
| Rectangle
Let 'a'
and 'b'
represent the length of two adjacent sides of a rectangle. The perimeter
of a rectangle is equal to 2 * [a+b], ( the length of one side added to
the length of an adjacent side, then multiplied by 2).
|
 |
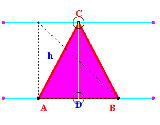 |
Triangle
Let 'AB'
represent the base of
the triangle, and 'CD'
represent the altitude (h).
The perimeter of a triangle is equal to the sum of the length of
the three sides [AB+BC+CA].
|
| Circle
*Terms to know: pi (p) is the ratio of the circumference to the diameter in all circles [pi always = 3.141...]; the diameter is the distance across a circle; and the radius is the distance from the center of a circle to any point on its edge). The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference which is equal to pi multiplied by the diameter (p* d). The area of a circle is equal to p* r2 (the length of the radius squared, then multiplied by 3.141...). |
 |
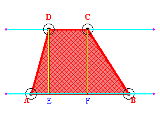 |
Trapezoid
Let 'ABCD'
represent a trapezoid where AB
and DC
are the bases;
DE
and
CF
are the altitudes (h).
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the length of all sides
[AB+BC+CD+DA].
|
| Polygons
Polygons are figures with many
sides and many angles (pentagon 5, hexagon 6, octagon 8). The perimeter
of a polygon is equal to the sum of the length of all sides [AB+BC+CD+DE+EA,
etc.].
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Inland Empire Job Corps San Bernardino, California |